- GST Council has approved a Goods and Services Tax (GST) two-tier rate structure — mainly 5% and 18% — effective 22 Sept 2025, with a special 40% slab and some items at 0%.
- Estimate: revenue loss of Rs 477 billion; major daily‑use items such as medicines, certain dairy and school stationery moved to 0% or lower slabs to help households.
- Businesses must update HSN/price lists, invoices and ERP before 22 Sept; consumers should check bills and plan purchases around the implementation date.
On Wednesday, the government announced a big change in India’s GST system, which has been in place since 2017. Taxes on many items like household essentials, medicines, small cars, and appliances have been reduced. This affects daily-use products such as toothpaste, insurance, tractors, and cement. The earlier four tax slabs of 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28% have now been cut down to just two – 5% and 18%. A special higher rate of 40% will still apply to a few items like luxury cars, tobacco, and cigarettes..
GST Council members met in Delhi and agreed, unanimously, to simplify GST slabs from four to mainly two: 5% and 18%, effective 22 September 2025. A special 40% slab remains for certain sin and luxury items, while a set of essentials and healthcare/education items moved to 0% (zero‑rated or exempt). The Council says revenue loss will be about Rs 477 billion from these changes. Implementation starts on 22 Sept 2025; transitional rules and compensation cess adjustments were also approved.
Full list: Items moved to 0% (zero-rated / exempt)
You’ll notice many common essentials and important health items now have no GST. Below is an easy‑to‑scan list grouped by category for quick reference.
- Life‑saving drugs and medicines: 33 life‑saving drugs, cancer medicines and certain medicines for rare diseases.
- Healthcare policies: Individual life insurance and personal health insurance policies (insured premiums where applicable).
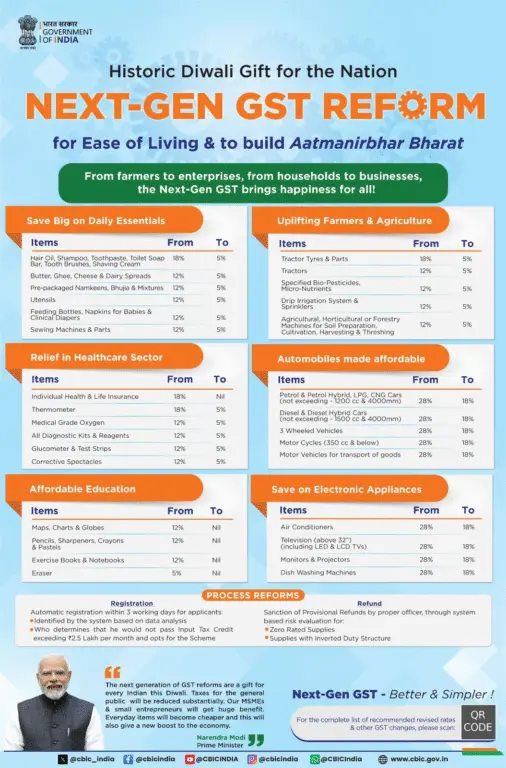
- School & stationery: Maps, charts, globes, pencils, sharpeners, crayons, pastels, exercise books, notebooks, erasers.
- Dairy & staples (selected, pre‑packaged): UHT milk, chena/paneer when pre‑packaged and labelled, pizza bread, khakhra, chapati/roti (pre‑packaged labelled forms).
- Other essential items: Select items declared urgently needed for public health and education as per CBIC notifications.
Full list: Items moved to 5% slab
Everyday personal care, basic food items, baby essentials, some medical devices and agricultural inputs are now at 5% to reduce household costs and help farmers.
- Personal care: Hair oil, shampoo, toothpaste, toilet soap, toothbrush, shaving cream.
- Dairy & packaged foods: Butter, ghee, cheese & dairy spreads, namkeens (packaged), basic utensils.
- Baby care: Feeding bottles, infant napkins, clinical diapers.
- Home & tools: Sewing machines and parts.
- Medical devices & diagnostics: Thermometers, medical grade oxygen, diagnostic kits and reagents, glucometers and test strips, corrective spectacles.
- Agriculture & farm machinery: Tractor tyres, tractor parts, tractors; specified bio‑pesticides, micro‑nutrients; drip irrigation systems and sprinklers; machines for soil preparation used in agriculture, horticulture or forestry.
Full list: Items moved to 18% slab
Items in this bracket are mid‑range consumer goods, transport, and many household durables. Expect moderate tax incidence here.
- Vehicles: Petrol & petrol hybrid cars (not exceeding 1200 cc & 4000 mm), diesel & diesel hybrid cars (not exceeding 1500 cc & 4000 mm), 3‑wheelers, motorcycles up to 350 cc, motor vehicles for goods transport.
- Home appliances & electronics: Air conditioners, televisions above 32″ (LED & LCD), monitors and projectors, dish washing machines.
- Farm & heavy machinery: Road tractors with engine capacity more than 1800 cc (placed here per list).
Full list: Items put in the new 40% special slab
High excise items, luxury goods and sin products now face a steep 40% GST. This is meant to curb consumption and preserve revenues.
- Tobacco & pan: Pan masala, cigarettes, gutka, chewing tobacco, bidis, smoking pipes.
- Sweetened & caffeinated drinks: Aerated waters with added sugar or flavour, caffeinated beverages, certain non‑alcoholic drinks.
- Luxury items & transport: Luxury vehicles, motorcycles exceeding 350 cc, aircraft for personal use, yachts, road tractors beyond specified limits.
- Firearms & betting: Revolvers and pistols, gambling (casinos), betting, horse racing, lotteries and online money gaming.
What this means for consumers: likely price and household budget impact
You should see noticeable savings on many daily items. Here are practical outcomes and simple worked examples so you can roughly gauge impact on your wallet.
- Daily soaps, shampoo, toothpaste: Moving to 5% from higher slabs will lower the final price. Example: a Rs 100 soap earlier taxed at 12% or 18% may now cost about Rs 105 (plus minor margins), instead of Rs 112–118 earlier.
- Milk and basic dairy: Selected UHT milk and paneer at 0% reduces shelf cost; for unpackaged local milk, check local VAT/levies which may still apply in some states during transition.
- Toothbrush & stationery: Many items now zero‑rated — expect visible price drops on school supplies for parents.
- Small cars and motorcycles: Cars within cc/length limits and motorcycles up to 350 cc at 18% may be cheaper than before if they were at 28% earlier. However, some cars may still attract compensation cess adjustments; check final on‑road quotes.
- Luxury goods & sodas: Expect steep price rise where items moved into 40% slab, for example high‑end cigarettes, sugary aerated drinks and luxury vehicles will carry much higher tax.
Also Read – Income Tax Act Replacement Bill 2025
GST New Rate List 2025
Key timing and transitional points you should know:
| Detail | Value / Note |
|---|---|
| Implementation date | 22 September 2025 (all GST returns and invoices from this date must follow new rates) |
| Estimated revenue impact | About Rs 477 billion (as stated by Council) |
| Special slab | 40% for select sin and luxury items; compensation cess adjustments possible |
| Transitional rules | CBIC will issue notifications on stock on hand, invoicing cut‑offs, time of supply and input credit reversal; follow CBIC & GST portal instructions closely |
| Official information | cbic.gov.in | gst.gov.in | gstcouncil.gov.in |
Practical transitional notes: suppliers must stamp invoices issued before 22 Sept at old rates; invoices issued on or after 22 Sept must use new slabs. Input tax credit (ITC) treatment will follow CBIC notifications — if unsure, keep documents and ask a tax advisor or contact the CBIC helpdesk.
How to verify the GST rate for a specific product (step-by-step)
- Find the HSN code on the product package or supplier invoice (ask your vendor if it’s missing).
- Search the HSN and GST rate on gst.gov.in or check CBIC circulars at cbic.gov.in. Use the GST rate finder or HSN list notifications.
- Confirm classification with your supplier and, if needed, request a written declaration on the HSN/rate used.
- For ambiguous products, check recent CBIC/GST Council notifications; rates changed on 22 Sept 2025 will be listed in official PDFs.
- If you’re still unsure, call the CBIC helpdesk or your GST practitioner. Keep records of these communications in case of audits.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) on the new two‑tier GST
- Q: Will online orders placed before 22 Sept but delivered after be taxed at old or new rate?
- A: Taxability depends on time of supply rules and invoice date. CBIC transitional notification will clarify; keep order and invoice dates handy and check supplier communication.
- Q: How is compensation cess handled for items that moved to lower slabs?
- A: The Council said compensation cess adjustments will be made. Exact cess rates and apportionment will be notified by CBIC and the finance ministry. Watch official releases at cbic.gov.in.
- Q: Can I claim ITC for goods bought before the change but sold after?
- A: Transitional rules will spell out ITC treatment. Keep invoices and follow CBIC guidance; in many cases you can still claim ITC subject to the usual conditions.
- Q: What about imports and customs duties?
- A: GST on imports follows IGST rules; customs duty remains separate. For post‑implementation classification, check CBIC customs notifications and tariff updates.
- Q: Where do I get official clarifications or help?
- A: Use cbic.gov.in, gst.gov.in and your state GST helpdesk. For Council releases see gstcouncil.gov.in.